-
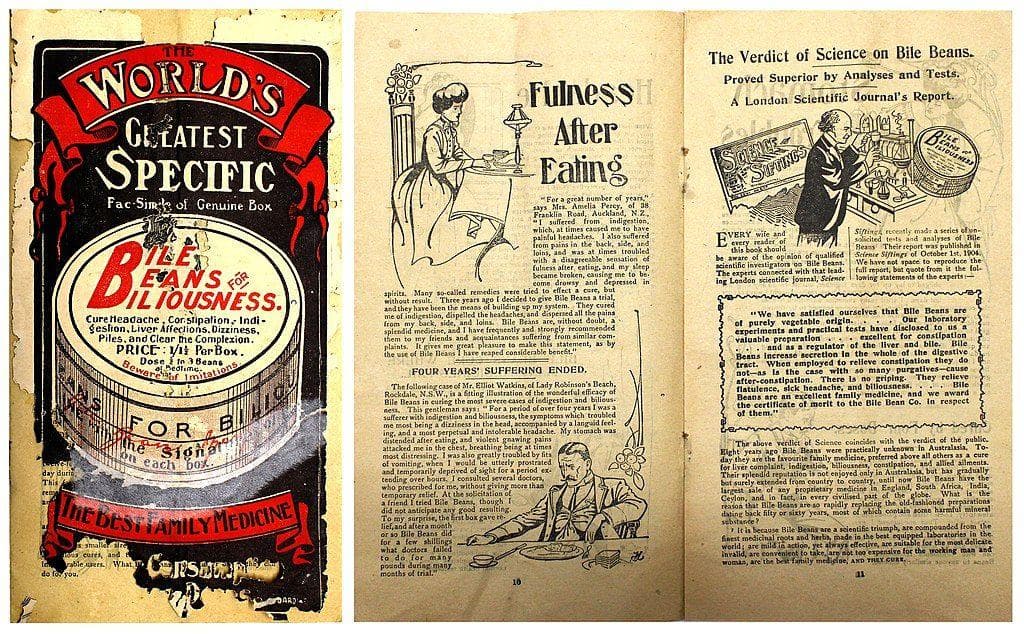
(#1) Clostridium difficile
Symptoms: Diarrhea, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain/tenderness
Fatal: No
Treatment Options: Antibiotics like metronidazole, vancomycin, or fidaxomicin
CDC Hazard Level: Urgent
C. difficile is a bacterial disease that can cause colitis, a condition in which the colon is inflamed and irritated. This bacteria is generally found in fecal matter and passes through contact, like touching a contaminated object and then touching your mouth or eyes. Elderly people and those who are already sick are more susceptible to contracting this disease, and people taking antibiotics are also at a higher risk. Studies have shown that some antibiotics used to treat some strains of C. difficile are becoming less effective, and the CDC has warned that these drug-resistant strains constitute an urgent hazard level.
-
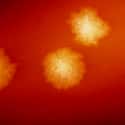
(#2) Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae
Symptoms: Fever, generally feeling unwell, rapid pulse, pain in heart
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Draining, certain antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Urgent
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) is the name given to a family of different germs that have proven difficult to treat with antibiotics, including diseases like E. coli. According the CDC, CRE bacteria have become nearly impossible to treat with most existing drugs. This is a major problem, as reports state that up to 50% of infections result in death. CRE can also exist inside a host body with no signs of infection, making it easier for the bacteria to spread. Generally, CRE is spread via person to person contact and most people become infected in hospital settings and generally overseas.
Some clinicians have reported the existence of strains that are resistant to all antibiotics, a chilling fact that has driven the CDC to label CRE as an urgent threat.
-
(#3) Gonorrhea
- Pelvic pain, Swollen testicle, Dysuria, Vaginal bleeding, Abdominal pain, Abnormal vaginal discharge, Penile discharge
Symptoms: Usually no symptoms, but can cause painful urination, vaginal bleeding, discharge from penis/vagina, swollen testicles, itching, soreness
Fatal: No
Treatment Options: Antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Urgent
Gonorrhea is an infamous STD that can be passed by vaginal, oral, and anal sex. It's an extremely common disease, the second most reported STD with 350,062 infections in 2014 alone. The disease can be extremely painful, although some people may get it and never show any outward symptoms. Women are especially unlikely to show symptoms. While it is traditionally treated with antibiotics, studies have shown that gonorrhea has become more resistant to these drugs over the years. Over 15% of tested bacterium showed a resistance to penicillin, once one of the most common and effective antibiotics. The resistance rate for other, less common antibiotics was even higher.
Long term infection can do serious damage, including making women infertile. Certain antibiotics can still be used to cure many strains, but more research is required to make sure this once curable disease remains that way.
-
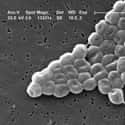
(#4) Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter
Symptoms: Pneumonia, bloodstream infections
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Colistin or tigecycline
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Roughly 500 have died as a result of multidrug-resistant acinetobacter, a form of gram-negative bacteria that can have serious impacts on your health. These bacteria can cause serious cases of pneumonia and bloodstream infections, and they can survive in hospital environments and be transmitted by medical staff. At the moment, colistin and tigecycline are the only antibiotics that are still able to fight off this disease. However, a colistin-resistant strain of acinetobacter has been identified in Europe.
-
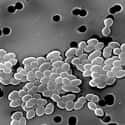
(#5) Drug-Resistant Campylobacter
Symptoms: Diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, temporary paralysis, nausea, vomiting, bloodstream infection
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Macrolides
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Campylobacter infections can be severe and cause flu-like symptoms easily initially mistaken for a milder infection. Two of the most commonly prescribed treatments are proving ineffective against new, drug-resistant strains. The bacteria is passed through contact with animals, and most infections are the result of exposure to raw chicken meat. Macrolide drugs are still the preferred treatment method, but they are becoming less effective. Campylobacter is spread from animals to people, usually via contaminated food. People who travel are more likely to be infected with a drug-resistant strain, and over 300,000 cases are reported annually.
-
(#6) Fluconazole-Resistant Candida Fungi
Symptoms: Bloodstream infection, yeast infection
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Limited
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Bacteria are not the only disease-causing organisms that are developing increased resistance to treatments. Fungi are as well. Antifungal medications are extremely valuable and usually effective at fighting disease, but one species has adapted to work around our existing treatments. Candida albicans, an infectious yeast, is the most likely cause for a type of fungal infection that easily causes complications. The infection can spread to many different parts of the body, including the bloodstream, where it can turn fatal. There are currently very few treatment options to deal with an antifungal-resistant infection of C. albicans, and many of them are toxic to patients who are already sick. More research is needed if we are to combat this issue. Luckily, however, antifungal resistance is still relatively uncommon.
-
(#7) Extended Spectrum Enterobacteriaceae
Symptoms: Varies by infected bacterium
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: β-lactam–β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, cephamycins, temocillin, various others
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Bacteria that carry a specific enzyme, Extended-spectrum β-lactamase, are being found to possess a resistance to two groups of antibiotics. Both penicillin and cephalosporin are used to treat many illnesses, but this enzyme might be making them obsolete. A wide variety of bacteria are susceptible to this enzyme, and infected bacterium are known as extended spectrum enterobacteriaceae (ESBLs). ESBLs can be extremely resilient even against powerful antibiotics, making it an alarming new hazard.
-
(#8) Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
Symptoms: Colonization, infections of the urinary tract and bloodstream
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Antibiotics other than vancomycin
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
As their name would suggest, VREs are strains of Enterococcus that have developed an immunity to the antibiotic vancomycin. Enterococci live in both the digestive system and the genital tract, and we all have them. Most of the time they are completely harmless, but they do have the ability to become infectious. When that happens, they can usually be treated with vancomycin. VREs are a different case, and must be combated with alternative antibiotics and can be more difficult to treat. While VRE infections can be fatal, less than 10% of infected patients in the United States die from them. People who've recently undergone surgery, have a weakened immune system, or use medical devices that stay in the body (like urinary or IV catheters) are more likely to become infected.
-
(#9) Pseudomonas infection
Symptoms: Ear infections, rashes, pneumonia, sepsis
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Case-specific antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common infection causing bacteria in the Pseudomonas genera. Each year, over 50,000 people become infected. Like many bacterial infections, Pseudomonas infections that originate in hospitals are becoming more difficult to treat. In cases of Multidrug-Resistant P. aeruginosa, each individual case must be lab tested in order to determine a viable antibiotic treatment. It is believed that up to 13% of all P. aeruginosa infections are now multidrug-resistant.
-
(#10) Salmonellosis
- Nausea, Fatigue, Abdominal pain, Rose spots, Vomiting, Headache, Hematochezia
Symptoms: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, bloodstream infection
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Fluoroquinolones, other antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
There are thousands of serotypes of salmonella, most of which spread via contact with objects contaminated by animal feces. Non-typhoidial salmonella is a specific strain that has an increased risk of blood infection, and many doctors are discovering cases that are extremely drug-resistant. Most cases are first treated with fluoroquinolones, but those are proving to be less effective than they were. People who have traveled outside of the United States are much more likely to contract a case of drug-resistant salmonellosis than infected persons who have never traveled. Luckily, the disease is rarely fatal, but it's more likely to cause deaths in the elderly and very young children.
-
(#11) Drug-Resistant Salmonella Serotype Typhi
Symptoms: Fever, abdominal pain, headache, bowl perforation, shock
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Vaccination (preventative), antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Another serotype of salmonella, this is the strain that causes typhoid fever. People in the developing world and those who travel there are at a higher risk of contracting typhoid fever, which can be fatal in some cases. Over 20 million people are infected with typhoid fever each year, making it an extremely important disease to study. Drug-resistance has been identified in multiple serotypes of salmonella, including the typhoid-inducing strains.
-
(#12) Drug-Resistant Shigella
Symptoms: Diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, reactive arthritis
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Usually unnecessary, antibiotics in extreme cases
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Shigellosis is caused by the shigella bacteria, and it can usually run its course after about a week. Drug-resistant shigella is a different story, however. These infections can last much longer and can be much more difficult to treat. Laboratory fecal testing is required to accurately diagnose the antibiotic-resistant strains, which can make treatment even more expensive.
-
(#13) Staphylococcus aureus
Symptoms: Sepsis, pneumonia, bloodstream infection
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Drainage, vancomycin, other functional antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Staphylococcus aureus is an incredibly common bacteria that has colonies in roughly 30% of the human population. The bacteria can cause a wide variety of symptoms and can be fatal if left untreated. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an extremely deadly strain that is antibiotic-resistant and killed more than 11,000 people in the United States annually. MRSA is becoming more common, leading the CDC to deem the disease a serious threat.
-
(#14) Drug-Resistant Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Symptoms: Pneumonia, meningitis, ear infections, sinus infections, bloodstream infections
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Vaccination (preventative), various antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Drug Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (DRSP) is a penicillin and other antibiotic-resistant bacterium that causes a variety of serious illnesses, some of which can be fatal. The bacteria can cause meningitis, which infects the brain and spinal cord. A vaccine exists to stop the spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae, and medical experts recommend the vaccine to prevent colonization. Excessive use of antibiotics is exacerbating the spread of this deadly bacterium.
-
(#15) Tuberculosis
- Dyspnea, Chronic cough, Night Sweats, Anorexia, Fatigue, Hemoptysis, Fever, Cough, Chills, Weight loss
Symptoms: Infection of the lungs and various other organs
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Tuberculosis is common throughout the world, and it can be extremely deadly. Tuberculosis is spread aerially and mostly infects the lungs, but it can infect other parts of the body including the brain. Drug-resistant TB is much more difficult to treat and can be an economic burden. Unless treated by an expert, this strain can be extremely resilient and end in a patient's death.
New Random Displays Display All By Ranking
About This Tool
Whether in medicine or agriculture, the abuse or overuse of antibiotics can lead to the emergence of multiple drug-resistant bacteria. Experts in the prevention and control of infectious diseases also pointed out that infectious diseases like Ebola cannot be eradicated because the virus still exists in animals. Drug resistance may occur with drug treatment. Drug-resistant diseases are the most dangerous, and vaccines must be used to eradicate infectious diseases.
For example, due to the overuse of drugs, the older generation of antibiotics has been unable to cure new potentially fatal infections. The random tool lists the 15 most dangerous drug-resistant diseases in the world.
Our data comes from Ranker, If you want to participate in the ranking of items displayed on this page, please click here.