-
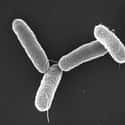
(#9) Pseudomonas infection
Symptoms: Ear infections, rashes, pneumonia, sepsis
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Case-specific antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common infection causing bacteria in the Pseudomonas genera. Each year, over 50,000 people become infected. Like many bacterial infections, Pseudomonas infections that originate in hospitals are becoming more difficult to treat. In cases of Multidrug-Resistant P. aeruginosa, each individual case must be lab tested in order to determine a viable antibiotic treatment. It is believed that up to 13% of all P. aeruginosa infections are now multidrug-resistant.
-
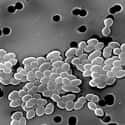
(#13) Staphylococcus aureus
Symptoms: Sepsis, pneumonia, bloodstream infection
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Drainage, vancomycin, other functional antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Staphylococcus aureus is an incredibly common bacteria that has colonies in roughly 30% of the human population. The bacteria can cause a wide variety of symptoms and can be fatal if left untreated. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an extremely deadly strain that is antibiotic-resistant and killed more than 11,000 people in the United States annually. MRSA is becoming more common, leading the CDC to deem the disease a serious threat.
-
(#4) Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter
Symptoms: Pneumonia, bloodstream infections
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Colistin or tigecycline
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Roughly 500 have died as a result of multidrug-resistant acinetobacter, a form of gram-negative bacteria that can have serious impacts on your health. These bacteria can cause serious cases of pneumonia and bloodstream infections, and they can survive in hospital environments and be transmitted by medical staff. At the moment, colistin and tigecycline are the only antibiotics that are still able to fight off this disease. However, a colistin-resistant strain of acinetobacter has been identified in Europe.
-
(#11) Drug-Resistant Salmonella Serotype Typhi
Symptoms: Fever, abdominal pain, headache, bowl perforation, shock
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Vaccination (preventative), antibiotics
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
Another serotype of salmonella, this is the strain that causes typhoid fever. People in the developing world and those who travel there are at a higher risk of contracting typhoid fever, which can be fatal in some cases. Over 20 million people are infected with typhoid fever each year, making it an extremely important disease to study. Drug-resistance has been identified in multiple serotypes of salmonella, including the typhoid-inducing strains.
-
(#1) Clostridium difficile
Symptoms: Diarrhea, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain/tenderness
Fatal: No
Treatment Options: Antibiotics like metronidazole, vancomycin, or fidaxomicin
CDC Hazard Level: Urgent
C. difficile is a bacterial disease that can cause colitis, a condition in which the colon is inflamed and irritated. This bacteria is generally found in fecal matter and passes through contact, like touching a contaminated object and then touching your mouth or eyes. Elderly people and those who are already sick are more susceptible to contracting this disease, and people taking antibiotics are also at a higher risk. Studies have shown that some antibiotics used to treat some strains of C. difficile are becoming less effective, and the CDC has warned that these drug-resistant strains constitute an urgent hazard level.
-
(#8) Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
Symptoms: Colonization, infections of the urinary tract and bloodstream
Fatal: Yes
Treatment Options: Antibiotics other than vancomycin
CDC Hazard Level: Serious
As their name would suggest, VREs are strains of Enterococcus that have developed an immunity to the antibiotic vancomycin. Enterococci live in both the digestive system and the genital tract, and we all have them. Most of the time they are completely harmless, but they do have the ability to become infectious. When that happens, they can usually be treated with vancomycin. VREs are a different case, and must be combated with alternative antibiotics and can be more difficult to treat. While VRE infections can be fatal, less than 10% of infected patients in the United States die from them. People who've recently undergone surgery, have a weakened immune system, or use medical devices that stay in the body (like urinary or IV catheters) are more likely to become infected.
New Random Displays Display All By Ranking
About This Tool
Whether in medicine or agriculture, the abuse or overuse of antibiotics can lead to the emergence of multiple drug-resistant bacteria. Experts in the prevention and control of infectious diseases also pointed out that infectious diseases like Ebola cannot be eradicated because the virus still exists in animals. Drug resistance may occur with drug treatment. Drug-resistant diseases are the most dangerous, and vaccines must be used to eradicate infectious diseases.
For example, due to the overuse of drugs, the older generation of antibiotics has been unable to cure new potentially fatal infections. The random tool lists the 15 most dangerous drug-resistant diseases in the world.
Our data comes from Ranker, If you want to participate in the ranking of items displayed on this page, please click here.